📜 End-to-End Security Chain of Custody Report: FEG SMaRTi™ Diamond Standard
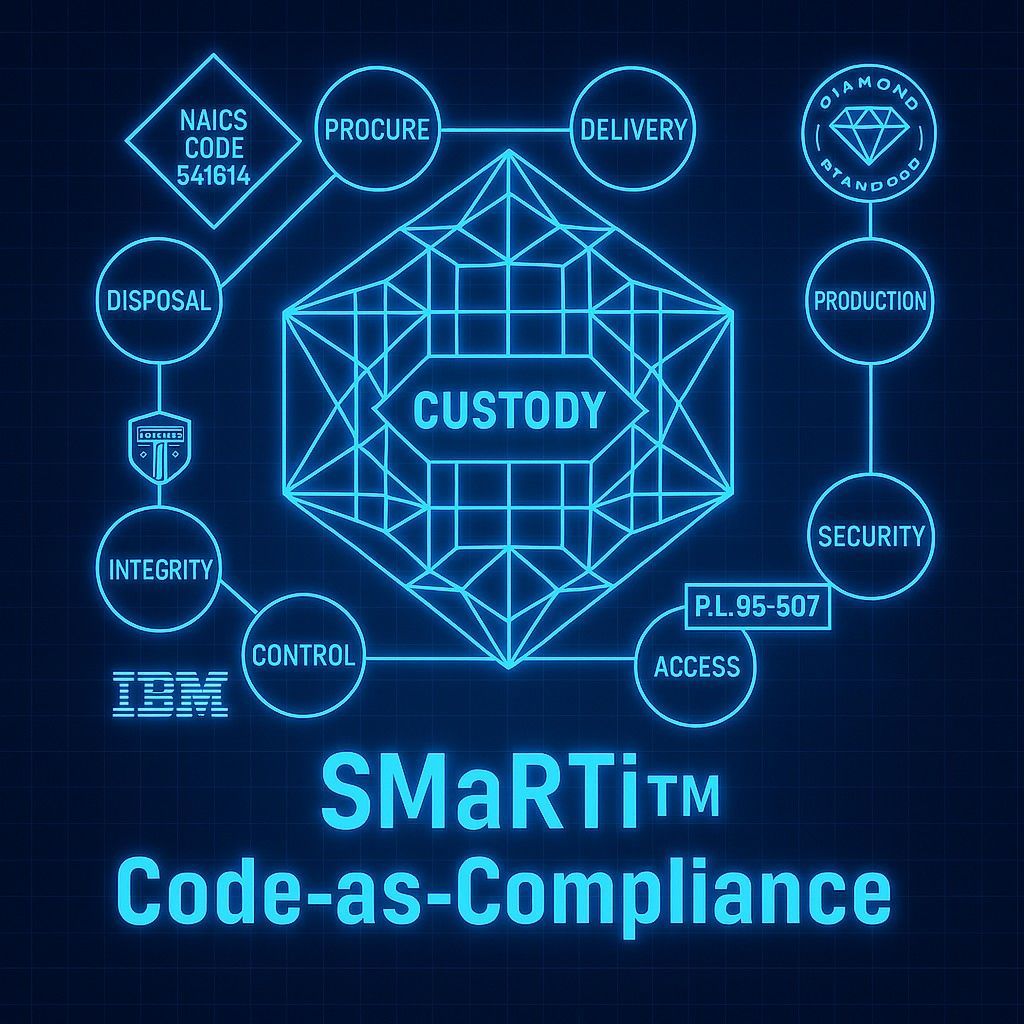
The FEG SMaRTi™ Diamond Standard for NAICS CODE 541614 5PL/MSP Invoice Optimization achieves supremacy security by implementing a five-stage, zero-trust security architecture. This architecture converts operational reality (IoT data) into liquid financial assets (QRE value) with cryptographic certainty, ensuring regulatory immutability and transactional finality across the entire IBM Cloud Ecosystem.
Stage 1: Source & Ingestion Security (The IoT Super Magnet)
This stage protects the data stream from the client's physical assets to the cloud processing environment.
- D-U-N-S Linked Identity Assurance: Every physical sensor or IoT system component (the "Super Magnet") is provisioned with an x.509 certificate cryptographically linked to the client's official D-U-N-S Number. This identity is validated by the ROKS cluster's ingress, ensuring only authorized, non-repudiable data sources are accepted.
- Encrypted Transport Layer: All operational telemetry (logistics costs, R&D activity) is transferred via TLS/SSL (mTLS) and authenticated messaging protocols (e.g., Kafka/MQTT) over the IBM Cloud Private Network. This enforces end-to-end encryption and eliminates exposure to public internet threats.
- MZR Deployment: The IoT ingestion endpoints are deployed across Multiple-Zone Regions (MZR), providing immediate geographic redundancy. This ensures that a local outage will not halt the continuous flow of data required to maintain the real-time QRE assessment.
Stage 2: Processing Integrity (OpenShift Code-as-Compliance)
This stage ensures the integrity of the proprietary SMaRTi™ algorithms and the resulting QRE valuation.
- Hyper Protect Key Management (KYOK): The master encryption keys for the entire platform are secured within IBM Hyper Protect Crypto Services (HPCS), certified to the FIPS 140-2 Level 4 standard. This Keep Your Own Key (KYOK) model guarantees that only FEG, and not the underlying cloud provider, can decrypt the sensitive optimization logic or client data.
- OpenShift Security Context Constraints (SCCs): The Code-as-Compliance OpenShift Operators are bound by stringent SCCs, restricting container privileges and preventing root access, lateral movement, or unauthorized modifications to the compliance logic.
- Image Signing and Verification: All SMaRTi™ container images are cryptographically signed. The ROKS cluster automatically verifies the signature before deployment, ensuring that only certified, tamper-proof code—containing the automated IRC §41(d) compliance logic—is executed.
- Runtime Isolation: OpenShift provides built-in network policies and micro-segmentation, isolating the SMaRTi™ financial processing microservices from the ingestion layer and the administrative control plane, preventing interference or data leakage.
Stage 3: Audit Immutability (Hyperledger Ledgering)
This stage converts the verified financial calculation into a permanent, legally binding asset.
- Cryptographic Finality: Once the SMaRTi™ engine calculates the maximum legal QRE value, the resulting Qualified Digital Invoice Format (QDIF) is hashed and committed to the Hyperledger Fabric. The resulting ledger block is chronologically chained and immutable, creating a zero-dispute audit record that Far Exceeds traditional paper records.
- Channel Isolation and Confidentiality: The Hyperledger network utilizes Channels to segregate sensitive client data. A client's QDIF is only visible to FEG and that specific client (and the eventual purchasing financial partner). This supremacy security measure prevents competing clients (in the "Book of Business" context) from viewing proprietary financial strategies or QRE values.
- Private Data Collections (PDCs): PDCs are used to store highly sensitive information, such as the full four-part IRC §41(d) justification narrative, off the main channel, ensuring that only the relevant auditor (FEG/Client) can access the granular compliance proof, while the QDIF transaction remains publicly auditable via its hash.
Stage 4: Financial Transaction Security (Uni-Multi-Railing)
This stage guarantees the security, privacy, and finality of the near-immediate transformation into liquidity.
- Uni-Multi-Railing Asset Finality: The Smart Contract governing the Uni-Multi-Railing auction enforces strict business logic: once a bid is accepted, the sale is executed instantly and immutably recorded on the Hyperledger. This mechanism mitigates counterparty risk by guaranteeing settlement at the time of the QDIF asset sale.
- Asymmetric Transaction Security: The "Multi-Railing" utilizes unique cryptographic identities for each financial channel (bank/investor). Each partner receives an offer on the QDIF asset but is strictly isolated from seeing the bids or liquidity reserves of the other financial partners.
- Zero-Risk Net-Settlement: The final security feature is the guaranteed application of the sale proceeds to the FEG 5PL Invoice. The entire transaction is secured by the ledger, ensuring that the real-time liquidity instantly covers the client's MSP costs, locking in the financial benefit without exposure to external bank transfer delays or failures.
The FEG Diamond Standard creates a closed, fully auditable loop, establishing a cryptographic chain of custody from the IoT sensor to the bank ledger. This end-to-end solution provides a level of financial security and regulatory certainty that is unprecedented in the logistics and consulting space.










